The World Avatar
A knowledge-graph-based digital twin of the world
A knowledge graph is a network of data expressed as a directed graph, where the nodes of the graph are concepts or their instances (data items) and the edges of the graph are links between related concepts or instances. Knowledge graphs are often built using the principles of Linked Data. They provide a powerful means to host, query and traverse data, and to find and retrieve related information.
The World Avatar project, with substantial contributions by CARES, CMCL, and CMPG, aims to create a digital ‘avatar’ of the real world. Its code is publicly available. The digital world is composed of a dynamic knowledge graph that contains concepts and data that describe the world, and an ecosystem of autonomous computational agents that simulate the behaviour of the world and that update the concepts and data so that the digital world remains current in time. In this manner, it is proposed that it is possible to create digital twins that are able to describe the behavior of complex systems, and by doing so provide the ability to make data-driven decisions about how to optimise the systems.
A central tenet of the World Avatar is the requirement to share data so that all the computational agents experience a self-consistent view of the world, and the requirement that data and computational agents must be interoperable across different technical and social domains. This interoperability, defined in the sense of the ability of tools and systems to understand and use the functionalities of other tools, is considered to be one of the key aspects of Industry 4.0 and will become increasingly important as the complexity and choice of tools inevitably increases. For example, considerations raised by recent reports concerning the possible role of hydrogen in the future UK energy landscape span the electrical power system, the gas grid, the potential of biomass, solar and wind energy, the transport system, heating of commercial and domestic buildings, in addition to considerations relating to the acceptance and adoption of new technologies by the public.
The World Avatar represents information in a dynamic knowledge graph using technologies from the Semantic Web stack. Unlike a traditional database, the World Avatar contains an ecosystem of autonomous computational agents that continuously update it.
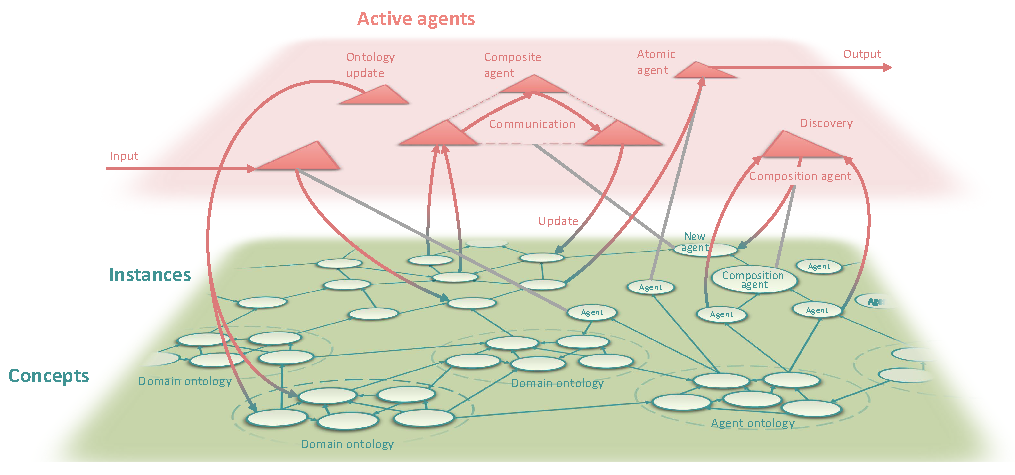
The main components of the dynamic knowledge graph are illustrated in the above figure. The dynamic knowledge graph contains concepts and instances that are linked to form a directed graph. The agents are described ontologically as part of the knowledge graph, and are able to perform actions on both concepts and instances. This confers versatility because it combines a design that enables agents to update and restructure the knowledge graph, with a structure that allows agents to discover and compose other agents simply by reading from and writing to the knowledge graph.
Recent Associated Preprints
325: Urban Vulnerability Assessment of Sea Level Rise in Singapore through The World Avatar
Shin Zert Phua, Kok Foong Lee, Yi-Kai Tsai, Srishti Ganguly, Jingya Yan, Sebastian Mosbach, Trina Ng, Aurel Moise, Benjamin P. Horton, and Markus Kraft, Technical Report 325, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge, 2024.
324: An analysis of renewable energy resources and options for the energy transition in Chile
Andrea M Oyarzún, Jiying Chen, George Brownbridge, Jethro Akroyd, and Markus Kraft, Technical Report 324, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge, 2024.
323: Impact of heat pumps and future energy prices on regional inequalities
Jieyang Xu, Sebastian Mosbach, Jethro Akroyd, and Markus Kraft, Technical Report 323, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge, 2024.
322: Hacking Decarbonisation with a Community-Operated CreatorSpace
Aleksandar Kondinski, Sebastian Mosbach, Jethro Akroyd, Andrew Breeson, Yong Ren Tan, Simon D. Rihm, Jiaru Bai, and Markus Kraft, Technical Report 322, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge, 2023.
Recent Associated Publications
Question-answering system for combustion kinetics
Laura Pascazio, Dan N. Tran, Simon D. Rihm, Jiaru Bai, Sebastian Mosbach, Jethro Akroyd, and Markus Kraft, Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 40, 105428, (2024).
Markus Hofmeister, Kok Foong Lee, Yi-Kai Tsai, Magnus Müller, Karthik Nagarajan, Sebastian Mosbach, Jethro Akroyd, and Markus Kraft, Energy and AI 17, 100376, (2024).
Dynamic knowledge graph approach for modelling the decarbonisation of power systems
Wanni Xie, Feroz Farazi, John Atherton, Jiaru Bai, Sebastian Mosbach, Jethro Akroyd, and Markus Kraft, Energy and AI 17, 100359, (2024).
Semantic agent framework for automated flood assessment using dynamic knowledge graphs
Markus Hofmeister, Jiaru Bai, George Brownbridge, Sebastian Mosbach, Kok Foong Lee, Feroz Farazi, Michael Hillman, Mehal Agarwal, Srishti Ganguly, Jethro Akroyd, and Markus Kraft, Data-Centric Engineering 5, 14, (2024).
Funding
This research was partly funded by the National Research Foundation (NRF), Prime Minister's Office, Singapore under its Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (CREATE) programme.