Technical Report 288, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge
Injection of charge from non-thermal plasma into a soot forming laminar coflow diffusion flame
Reference: Technical Report 288, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge, 2022
- Ethylene coflow diffusion flame with charge injection was reported for the first time
- Flames with injected charge retained the classical flame shape
- The soot volume fraction decreases with increasing charge injection into the flame
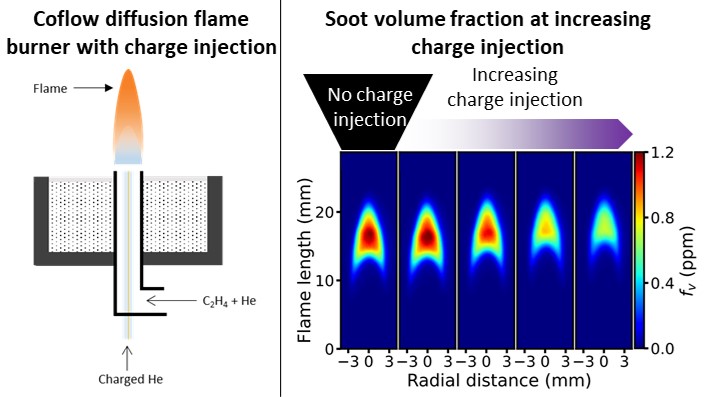 A novel, modified Yale Steady Flame burner was developed to study the effect of charge injection from a non-thermal plasma into three helium-diluted laminar coflow diffusion ethylene flames. The frequency of the high voltage (HV) signal was varied to control the ion concentration injected into the flames. Optical emission spectroscopy was used to characterise the non-thermal plasma while a bias plate methodology was used to gauge the relative amount of charge generated. For different HV signal frequencies, the laser-induced fluorescence of OH*, chemiluminescence of CH*, and laser-induced incandescence of soot in flames were measured. The OH*
and CH* measurements showed that the flames with the injected charge retained the classic flame shape. This is significant because it can facilitate the study of the effect of charge on the formation of soot in flames. Soot reduction was found to be significant at low HV signal frequencies corresponding to an increase in the amount of the relative charge injection. The soot reduction decreased when the HV signal frequency increased, which corresponded to a drop in the concentration of the ion concentration. Notably, at low HV signal frequency, the magnitude of soot reduction in high concentrated (60%) ethylene flame is three times lower than that of the less concentrated (32%) ethylene flame. This can be attributed to the decrease in the ratio of charge injected to soot precursor concentration when the concentration of the ethylene flame is increased. These results demonstrate that the current system is a promising candidate for studying the effect of the charge from non-thermal plasma on soot formation in laminar coflow diffusion flames.
A novel, modified Yale Steady Flame burner was developed to study the effect of charge injection from a non-thermal plasma into three helium-diluted laminar coflow diffusion ethylene flames. The frequency of the high voltage (HV) signal was varied to control the ion concentration injected into the flames. Optical emission spectroscopy was used to characterise the non-thermal plasma while a bias plate methodology was used to gauge the relative amount of charge generated. For different HV signal frequencies, the laser-induced fluorescence of OH*, chemiluminescence of CH*, and laser-induced incandescence of soot in flames were measured. The OH*
and CH* measurements showed that the flames with the injected charge retained the classic flame shape. This is significant because it can facilitate the study of the effect of charge on the formation of soot in flames. Soot reduction was found to be significant at low HV signal frequencies corresponding to an increase in the amount of the relative charge injection. The soot reduction decreased when the HV signal frequency increased, which corresponded to a drop in the concentration of the ion concentration. Notably, at low HV signal frequency, the magnitude of soot reduction in high concentrated (60%) ethylene flame is three times lower than that of the less concentrated (32%) ethylene flame. This can be attributed to the decrease in the ratio of charge injected to soot precursor concentration when the concentration of the ethylene flame is increased. These results demonstrate that the current system is a promising candidate for studying the effect of the charge from non-thermal plasma on soot formation in laminar coflow diffusion flames.
PDF (2.3 MB)