Technical Report 194, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge
Sooting characteristics of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether blends with diesel in a diffusion flame
Reference: Technical Report 194, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge, 2017
- The smoke points of diesel blends with PODEn and several other oxygenated hydrocarbon additives were measured with a diffusion flame.
- Sooting propensity of all the oxygenated blends exhibited similar results.
- Oxygen content effect was found to have limited impact in comparison to dilution effect for soot suppression.
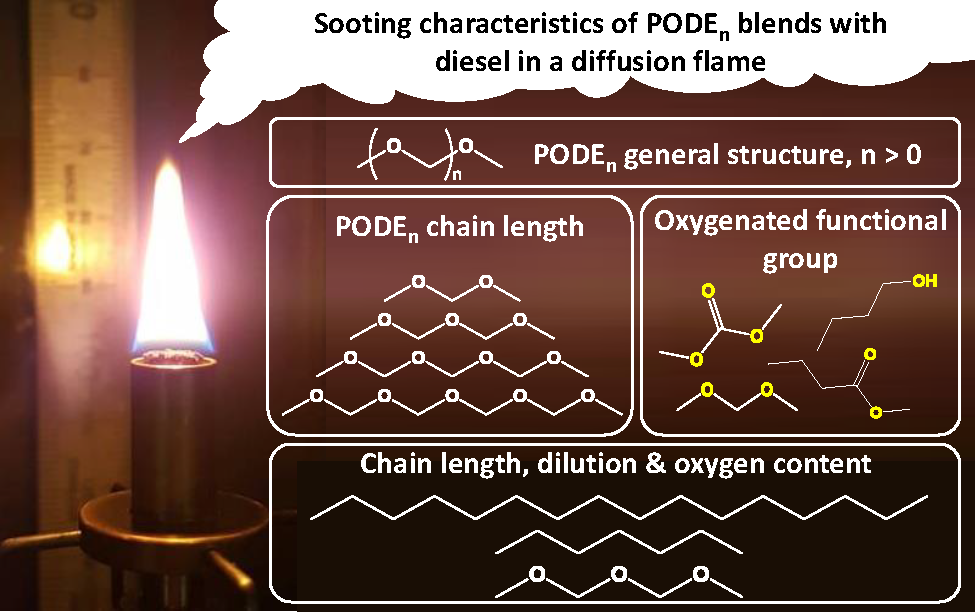 In this paper, we investigate the sooting propensity of PODEn/diesel blends.
The sooting characteristics of PODEn/diesel blends are determined using a standard ASTM D1322 smoke point lamp. The performance of PODEn with different chain length (addition of -CH2O- units) is benchmarked against other oxygenated soot suppression additives, including esters (methyl butyrate), carbonates (dimethyl carbonate) and alcohols (n-butanol). Soot reduction induced by the dilution of the aromatic fraction in the diesel fuel was found to have the biggest impact, followed by soot reduction by decreasing the hydrocarbon chain length and to a lesser extent increasing the oxygen content. The reason for the limited influence of oxygen content on soot suppression was further explored by examining the possible decomposition pathways and products of the different additives.
In this paper, we investigate the sooting propensity of PODEn/diesel blends.
The sooting characteristics of PODEn/diesel blends are determined using a standard ASTM D1322 smoke point lamp. The performance of PODEn with different chain length (addition of -CH2O- units) is benchmarked against other oxygenated soot suppression additives, including esters (methyl butyrate), carbonates (dimethyl carbonate) and alcohols (n-butanol). Soot reduction induced by the dilution of the aromatic fraction in the diesel fuel was found to have the biggest impact, followed by soot reduction by decreasing the hydrocarbon chain length and to a lesser extent increasing the oxygen content. The reason for the limited influence of oxygen content on soot suppression was further explored by examining the possible decomposition pathways and products of the different additives.
Material from this preprint has been published in Fuel.
PDF (1.8 MB)