Technical Report 171, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge
A Big Data Framework to Validate Thermodynamic Data for Chemical Species
Reference: Technical Report 171, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge, 2016
- Automated global cross-validation of large data sets of thermodynamic data.
- Evaluated reliability of the standard enthalpies of formation for 920 hydrocarbon-based species.
- Informed estimate of the standard enthalpy of formation is calculated using error-cancelling-balanced reactions.
- Automated identification and exclusion of unreliable data.
- Rapid convergence of the calculations towards chemical accuracy.
- Recommend future experiments and calculations for unreliable species.
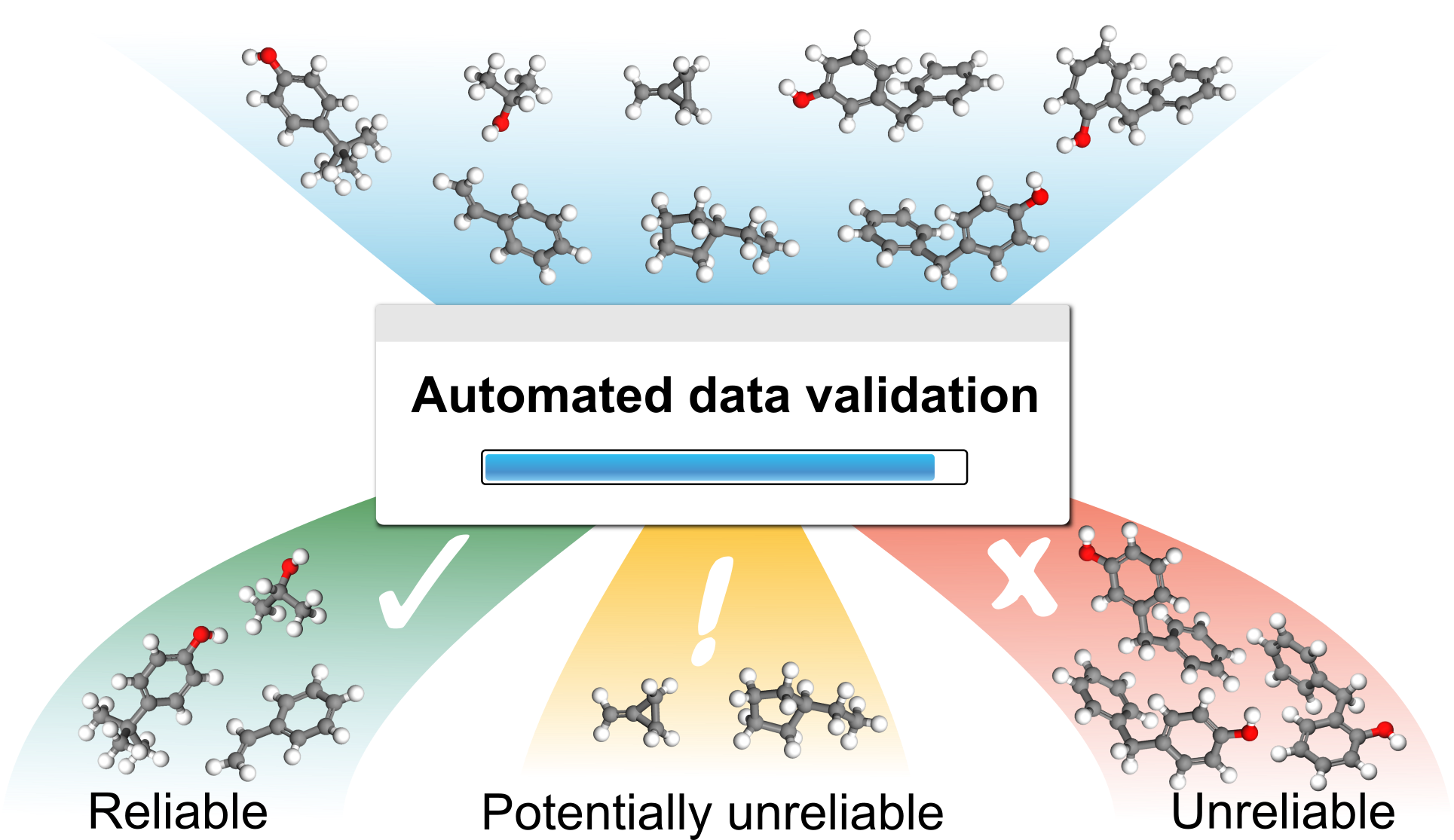 The advent of large sets of chemical and thermodynamic data has enabled the rapid investigation of increasingly complex systems. The challenge, however, is how to validate such large databases. We propose an automated framework to solve this problem by identifying which data are reliable and recommending what future experiments or calculations are required. The framework is applied to validate data for the standard enthalpy of formation for 920 hydrocarbon species retrieved from the NIST Chemistry WebBook. The concept of error-cancelling balanced reactions is used to calculate a distribution of possible values for the standard enthalpy of formation of each species. The method automates the identification and exclusion of unreliable data. We find that this enables the rapid convergence of the calculations towards chemical accuracy. The method can exploit knowledge of the structural similarities between species and the reliability of the data to identify which species introduce the most error and recommend what future experiments and calculations should be considered.
The advent of large sets of chemical and thermodynamic data has enabled the rapid investigation of increasingly complex systems. The challenge, however, is how to validate such large databases. We propose an automated framework to solve this problem by identifying which data are reliable and recommending what future experiments or calculations are required. The framework is applied to validate data for the standard enthalpy of formation for 920 hydrocarbon species retrieved from the NIST Chemistry WebBook. The concept of error-cancelling balanced reactions is used to calculate a distribution of possible values for the standard enthalpy of formation of each species. The method automates the identification and exclusion of unreliable data. We find that this enables the rapid convergence of the calculations towards chemical accuracy. The method can exploit knowledge of the structural similarities between species and the reliability of the data to identify which species introduce the most error and recommend what future experiments and calculations should be considered.
Material from this preprint has been published in Combustion and Flame.
PDF (6.4 MB)