Vapor pressure and heat of vaporization of molecules that associate in the gas phase
Highlights
- A model of vapour-liquid 1-component equilibrium with vapour dimerization.
- Predicts analytically vapour pressure, vaporization heat and dimer fraction vs. T.
- No fitting - input is 6 standard handbook thermodynamic parameters only.
- Reversely, accurate thermodynamic parameters obtained from vapour pressure data.
- High precision for fuel components under cylinder conditions.
Abstract
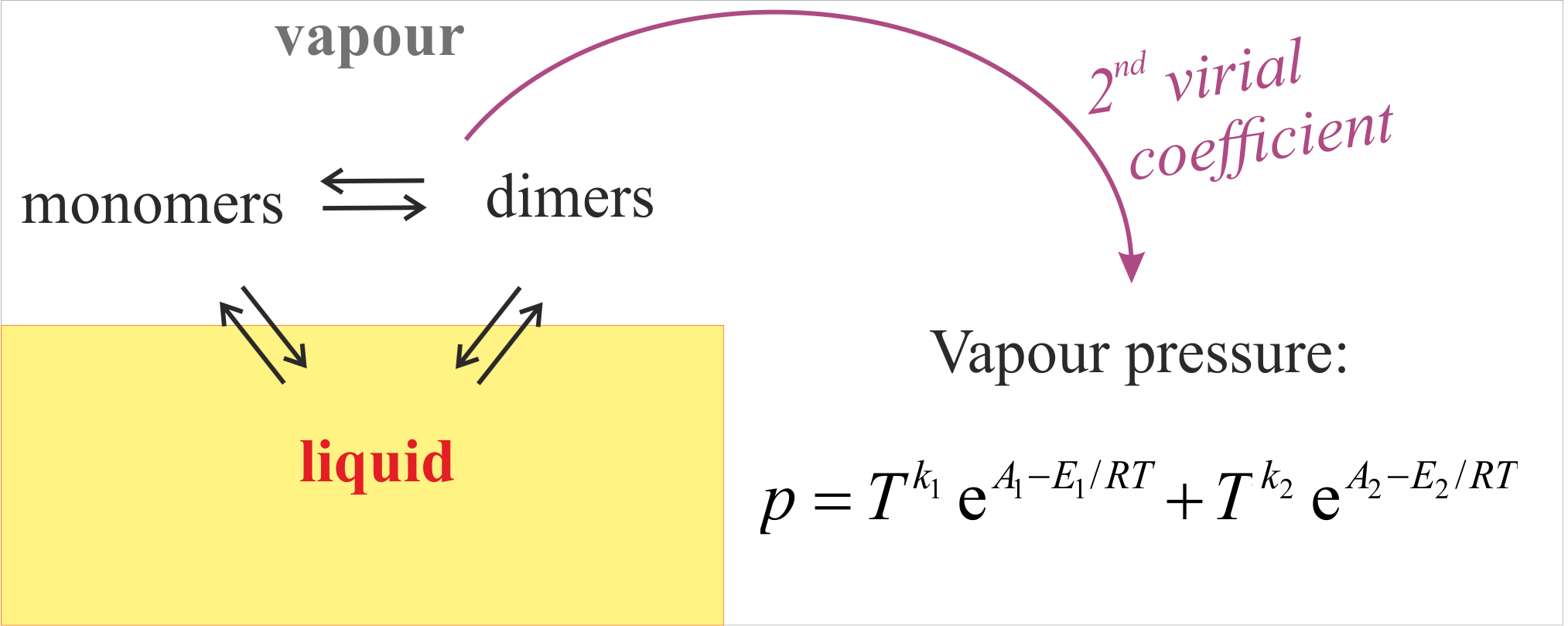 A model of the temperature dependence of the vapor pressure and the heat of vaporization of liquids whose vapors contain associates is presented for two cases: dimers and linear associates in the gas phase. The results are analytic generalizations of the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, valid with accuracy of 0.1%-1%, as demonstrated with 11 liquids: formic and acetic acids, methanol, ethanol, n-propanol, n-butanol, water, benzene, toluene, heptane, and iso-octane. The model involves only readily available handbook parameters: the room-temperature heat of vaporization, vapor pressure, heat capacities, second virial coefficient, and heat of dissociation of the dimers in the gas phase.
A model of the temperature dependence of the vapor pressure and the heat of vaporization of liquids whose vapors contain associates is presented for two cases: dimers and linear associates in the gas phase. The results are analytic generalizations of the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, valid with accuracy of 0.1%-1%, as demonstrated with 11 liquids: formic and acetic acids, methanol, ethanol, n-propanol, n-butanol, water, benzene, toluene, heptane, and iso-octane. The model involves only readily available handbook parameters: the room-temperature heat of vaporization, vapor pressure, heat capacities, second virial coefficient, and heat of dissociation of the dimers in the gas phase.
Access options
- This paper draws from preprint 190: Vapour pressure and vaporization heat of molecules able to dimerize
- Access the article at the publisher: DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b04241