Bivariate extension of the moment projection method for the particle population balance dynamics
- A bivariate moment projection method (BVMPM) for solving the two-dimensional population balance equation is developed.
- A two-dimensional Blumstein-Wheeler algorithm is proposed to track the number of the smallest particles.
- This method has been shown to be of high accuracy for modelling particles processes including inception, growth, shrinkage, coagulation and fragmentation.
- The method developed has the advantages of ease of implementation and numerical robustness.
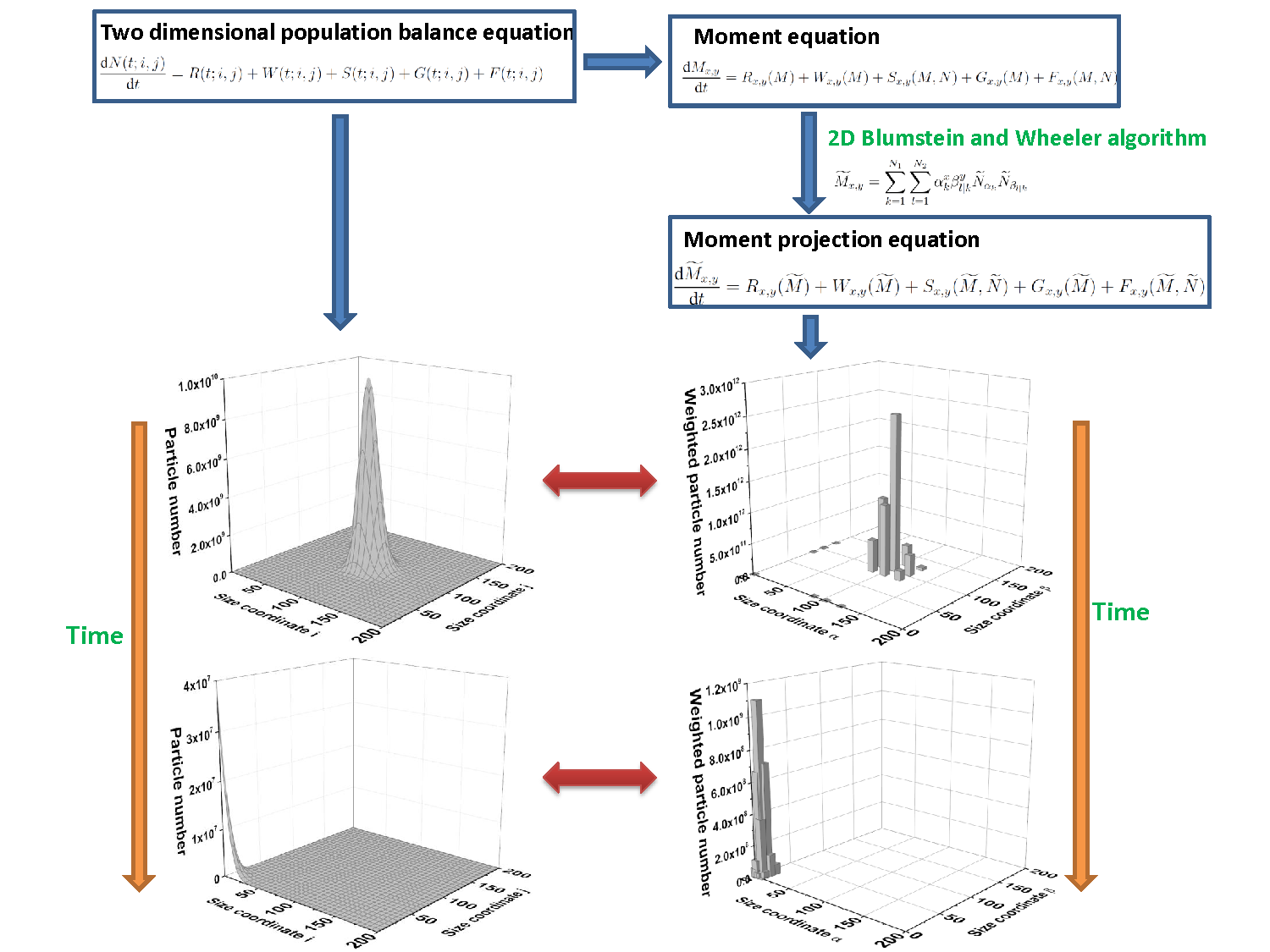 This work presents a bivariate extension of the moment projection method (BVMPM) for solving the two-dimensional population balance equations involving particle inception, growth, shrinkage, coagulation and fragmentation. A two-dimensional Blumstein and Wheeler algorithm is proposed to generate a set of weighted particles that approximate the number density function. With this algorithm, the number of the smallest particles can be directly tracked, closing the shrinkage and fragmentation moment source terms. The performance of BVMPM has been tested against the hybrid method of moments (HMOM) and the stochastic method. Results suggest that BVMPM can achieve higher accuracy than HMOM in treating shrinkage and fragmentation processes where the number of the smallest particles plays an important role.
This work presents a bivariate extension of the moment projection method (BVMPM) for solving the two-dimensional population balance equations involving particle inception, growth, shrinkage, coagulation and fragmentation. A two-dimensional Blumstein and Wheeler algorithm is proposed to generate a set of weighted particles that approximate the number density function. With this algorithm, the number of the smallest particles can be directly tracked, closing the shrinkage and fragmentation moment source terms. The performance of BVMPM has been tested against the hybrid method of moments (HMOM) and the stochastic method. Results suggest that BVMPM can achieve higher accuracy than HMOM in treating shrinkage and fragmentation processes where the number of the smallest particles plays an important role.
- This paper draws from preprint 198: Bivariate extension of the moment projection method for the particle population balance dynamics
- Access the article at the publisher: DOI: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2018.12.011