Technical Report 273, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge
Semantic 3D City Database - an enabler for a dynamic geospatial knowledge graph
Reference: Technical Report 273, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge, 2021
- OntoCityGML based on CityGML 2.0 and W3C standards.
- Architecture definition for a dynamic geospatial knowledge graph enabled by the Semantic 3D City Database.
- Data interoperability capabilities provided by means of sustainable digitisation practices.
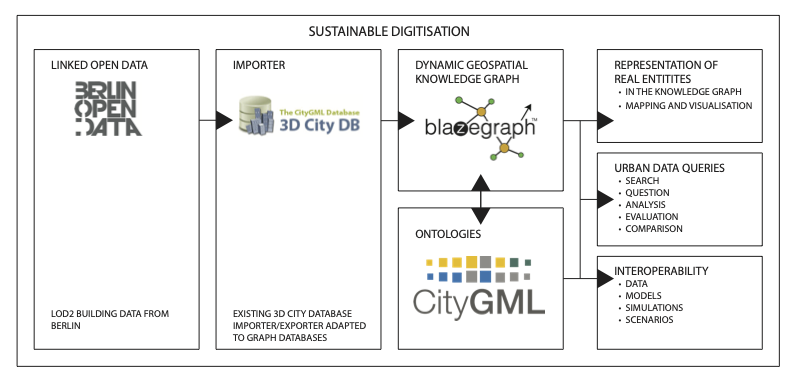 This paper presents a dynamic geospatial knowledge graph as part of The World Avatar project, with an underlying ontology based on CityGML 2.0 for three-dimensional geometrical city objects. We comprehensively evaluated, repaired and refined an existing CityGML ontology to produce an improved version that could pass the necessary tests and complete unit test development. A corresponding data transformation tool, originally designed to work alongside CityGML, was extended. This allowed for the transformation of original data into a form of semantic triples. We compared various scalable technologies for this semantic data storage and chose Blazegraph™ as it provided the required geospatial search functionality. We also evaluated scalable hardware data solutions and file systems using the publicly available CityGML 2.0 data of Charlottenburg in Berlin, Germany as a working example. The structural isomorphism of the CityGML schemas and the OntoCityGML Tbox allowed the data to be transformed without loss of information. Efficient geospatial search algorithms allowed us to retrieve building data from any point in a city using coordinates. The use of named graphs and namespaces for data partitioning ensured the system performance stayed well below its capacity limits. This was achieved by using scalable and dedicated data storage hardware capable of hosting expansible file systems, which strengthened the architectural foundations of the target system.
This paper presents a dynamic geospatial knowledge graph as part of The World Avatar project, with an underlying ontology based on CityGML 2.0 for three-dimensional geometrical city objects. We comprehensively evaluated, repaired and refined an existing CityGML ontology to produce an improved version that could pass the necessary tests and complete unit test development. A corresponding data transformation tool, originally designed to work alongside CityGML, was extended. This allowed for the transformation of original data into a form of semantic triples. We compared various scalable technologies for this semantic data storage and chose Blazegraph™ as it provided the required geospatial search functionality. We also evaluated scalable hardware data solutions and file systems using the publicly available CityGML 2.0 data of Charlottenburg in Berlin, Germany as a working example. The structural isomorphism of the CityGML schemas and the OntoCityGML Tbox allowed the data to be transformed without loss of information. Efficient geospatial search algorithms allowed us to retrieve building data from any point in a city using coordinates. The use of named graphs and namespaces for data partitioning ensured the system performance stayed well below its capacity limits. This was achieved by using scalable and dedicated data storage hardware capable of hosting expansible file systems, which strengthened the architectural foundations of the target system.
Material from this preprint has been published in Energy and AI.
PDF (983.4 KB)