Technical Report 143, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge
Solid-liquid transitions in homogenous ovalene, hexabenzocoronene and circumcoronene clusters: A molecular dynamics study
Reference: Technical Report 143, c4e-Preprint Series, Cambridge, 2014
- Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations of clusters of ovalene, hexabenzocoronene, and circumcoronene molecules are conducted.
- The bulk melting point of peri-condensed Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) is found to be linearly related to their size.
- A phase diagram is constructed which classifies the phase of a cluster into three regions: liquid, size-dependent, and solid.
- The critical PAH size in nascent and mature soot particles in the solid state is found as C78H22 and C54H18 at 1500 K respectively.
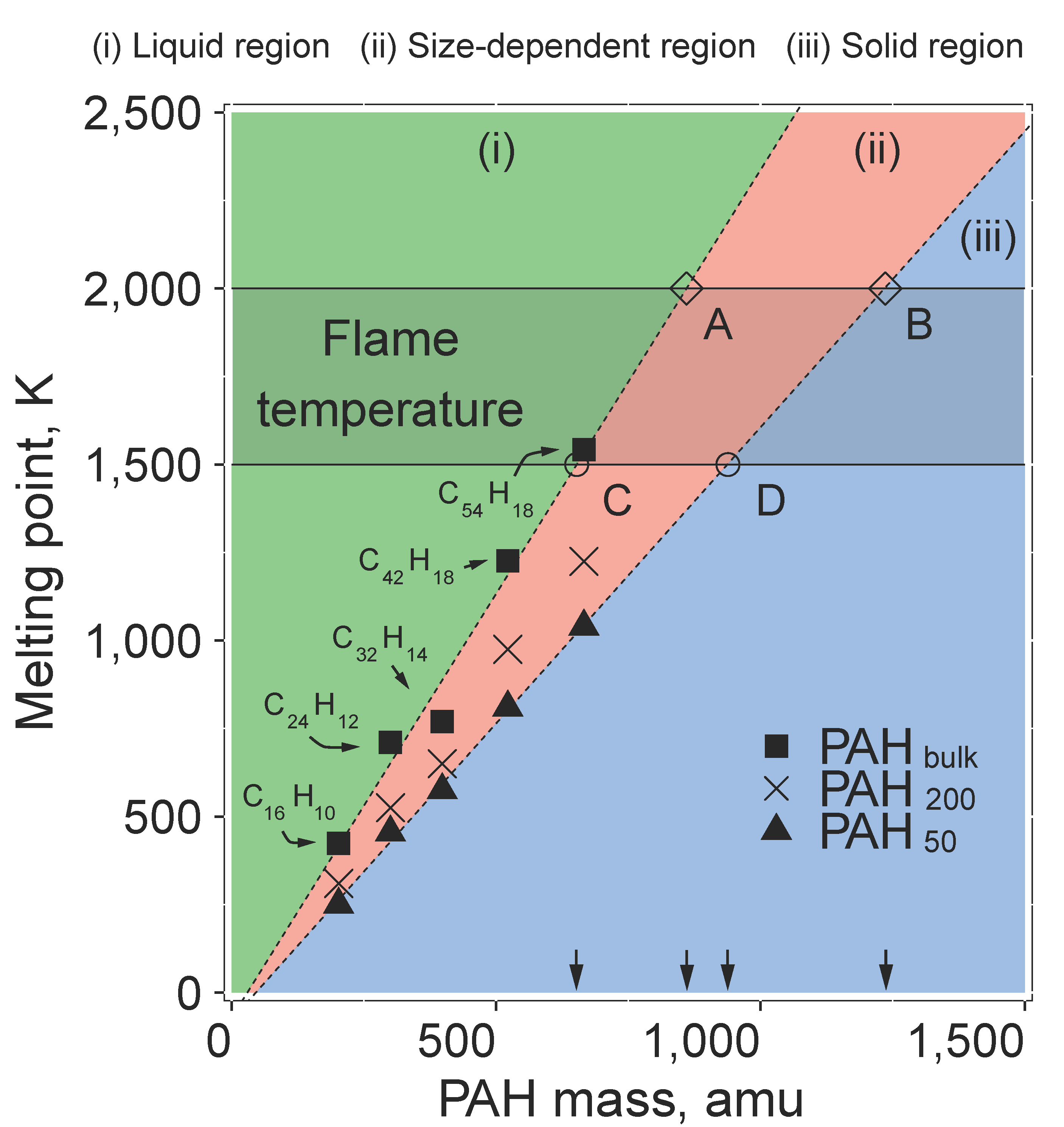 The melting behavior of ovalene (C32H14), hexabenzocoronene (C42H18) and circumcoronene (C54H18) clusters is analyzed using molecular dynamics simulations. The evolution of the intermolecular energy and the Lindemann Index is used to determine the cluster melting points. The bulk melting point of each material is estimated by linear extrapolation of the cluster simulation data. The value obtained for ovalene is in good agreement with the phase-transition temperature determined by experiment. We find that the bulk melting point of peri-condensed PAHs is linearly related to their size. The extrapolated hexabenzocoronene and circumcoronene bulk melting points agree with this linear relationship very well. A phase diagram is constructed which classifies the phase of a cluster into three regions: a liquid region, a size-dependent region and a solid region according to the size of the PAHs which build up the cluster. The size-dependent region highlights the range where the phase of a cluster also depends on the cluster size. Due to the similar size and density, a cluster with 50 molecules is considered an analogue for nascent soot particles whilst the bulk system of PAH molecules is seen as an approximation to mature soot particles. A detailed investigation of the phase diagram reveals that the critical size for nascent and mature soot particles in the solid state is C78H22 and C54H18 at 1500K respectively.
The melting behavior of ovalene (C32H14), hexabenzocoronene (C42H18) and circumcoronene (C54H18) clusters is analyzed using molecular dynamics simulations. The evolution of the intermolecular energy and the Lindemann Index is used to determine the cluster melting points. The bulk melting point of each material is estimated by linear extrapolation of the cluster simulation data. The value obtained for ovalene is in good agreement with the phase-transition temperature determined by experiment. We find that the bulk melting point of peri-condensed PAHs is linearly related to their size. The extrapolated hexabenzocoronene and circumcoronene bulk melting points agree with this linear relationship very well. A phase diagram is constructed which classifies the phase of a cluster into three regions: a liquid region, a size-dependent region and a solid region according to the size of the PAHs which build up the cluster. The size-dependent region highlights the range where the phase of a cluster also depends on the cluster size. Due to the similar size and density, a cluster with 50 molecules is considered an analogue for nascent soot particles whilst the bulk system of PAH molecules is seen as an approximation to mature soot particles. A detailed investigation of the phase diagram reveals that the critical size for nascent and mature soot particles in the solid state is C78H22 and C54H18 at 1500K respectively.
Material from this preprint has been published in Combustion and Flame.
PDF (5.8 MB)